Blockchain is one of the most revolutionary technologies of the 21st century. It is best known as the foundation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but its uses go far beyond digital money. For beginners, blockchain may sound technical, yet the idea is actually very simple. At its core, it is just a digital record system that is secure, transparent, and decentralized.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is like a digital ledger or notebook that records information. Unlike a traditional notebook, blockchain data is not stored in one place. Instead, it is spread across many computers around the world. Each entry in this ledger is called a block, and these blocks are connected together in a chain, which is why the system is called a blockchain.
Each block contains three main things: data (such as transactions), a unique code called a hash, and the hash of the block before it. This connection makes the blockchain secure, because if someone tries to change one block, all the following blocks will also need to be changed. In practice, this is nearly impossible.
How Does Blockchain Work?
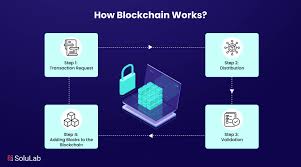
When a transaction, such as sending cryptocurrency, takes place, it is first broadcast to a network of computers. These computers, called nodes, check and verify the transaction. Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a block. This block is then added to the existing chain in a way that cannot be changed or deleted.
Because every participant in the network has a copy of the blockchain, it is decentralized. This means no single authority, such as a bank or government, controls it. Everyone can see the transactions, which makes it transparent and trustworthy.
Uses Beyond Cryptocurrency
Although blockchain became popular because of Bitcoin, its uses now go far beyond cryptocurrencies. Many industries are exploring blockchain to improve efficiency and security. For example, in supply chain management, blockchain can track products from the factory to the store, ensuring transparency. In healthcare, it can be used to store patient records safely. Even governments are considering blockchain to secure voting systems.
The Advantages of Blockchain
One of the main benefits of blockchain is security. Since every transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, it is very hard to tamper with. Another advantage is transparency, as all transactions are visible to participants in the network. Blockchain also reduces the need for middlemen, saving both time and money.
Challenges of Blockchain
Despite its advantages, blockchain faces challenges. The technology is still new, and many people find it difficult to understand. It also requires a lot of computer power, especially in systems like Bitcoin mining, which raises concerns about energy use. Additionally, governments are still developing laws to regulate blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion
Blockchain is more than just the technology behind Bitcoin. It is a new way of recording and sharing information that is secure, transparent, and decentralized. As the world moves towards digital transformation, blockchain will likely play a major role in industries far beyond finance.